Subsection 10.6.6 Carnot’s Heat Engine
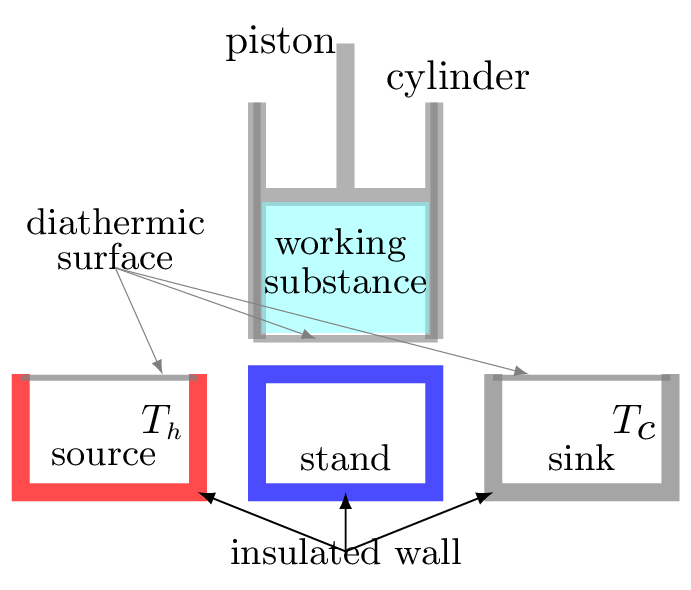
Carnot’s Assumption: Heat cannot be taken in at a certain temperature and converted to work with no other change in the system of surroundings. Carnot presented theoretically an ideal heat engine, free from all imperfection of actual engines. The engine operates between source and sink each of which is maintained at constant temperature. The engine is known as a Caront’s engine and its cycle of operation as the Carnot’s cycle. The schematics of engine is shown in Figure 10.6.6. The working substance is an ideal gas contained in an insulated cylinder with conducting bottom surface. A hot body of high thermal capacity maintained at a constant temperature \(T_{h} \,K\) serves as a source. A cold body maintained at a constant temperature \(T_{c} \,K \) serves as a sink. A stand has a perfectly insulated wall.
The cylinder can be moved in cycle from source, stand, sink, stand, and back to source without doing any work.
