Section 1.1 Physical Quantities
There are three fundamental physical quantities, length, mass, and time which are independent to one another. However, to completely express our daily life physical events these three quantities would not be sufficient so some more physical quantities were included later in the list of fundamental quantity and are altogether known as the base quantities. Their units are called fundamental or base units. The units of all other physical quantities can be expressed as combinations of the base units. Such units obtained for the physical quantities are called the derived units. A complete set of these units, both the base units and derived units, is known as the system of units. The diverse human history and geo-political issues gave birth to many systems of units some of them are now obsolete and some of them are still in use at different parts of world. The three different systems of units are considered here for discussion. They are FPS (foot pound second), MKS (meter kilogram second) systems, and CGS (centimeter gram second). The FPS system of units is also called British system and MKS system is also called a metric system. The metric system is a decimalized system of measurement developed in France in late \(18^{th}\) century. Since the metric system is almost universally used, it is often referred to as the International System of Units and abbreviated SI. Since SI units use decimal system, unit conversion within the system is quite simple and convenient. The systems of units are summarized in table 1.1.
| Physicqal Quantity | SI Units | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| Length | Meter | m |
| Mass | Kilogram | kg |
| Time | Second | s |
| Electric Current | Ampere | A |
| Temperature | Kelvin | K |
| Amount of substance | Mole | mol |
| Luminous Intensity | Candela | cd |
| Plane Angle | Radian | rad |
| Solid Angle | steradian | sterad |
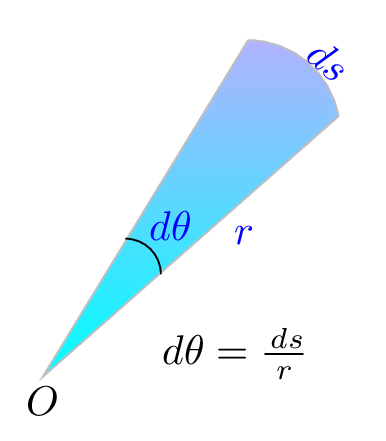
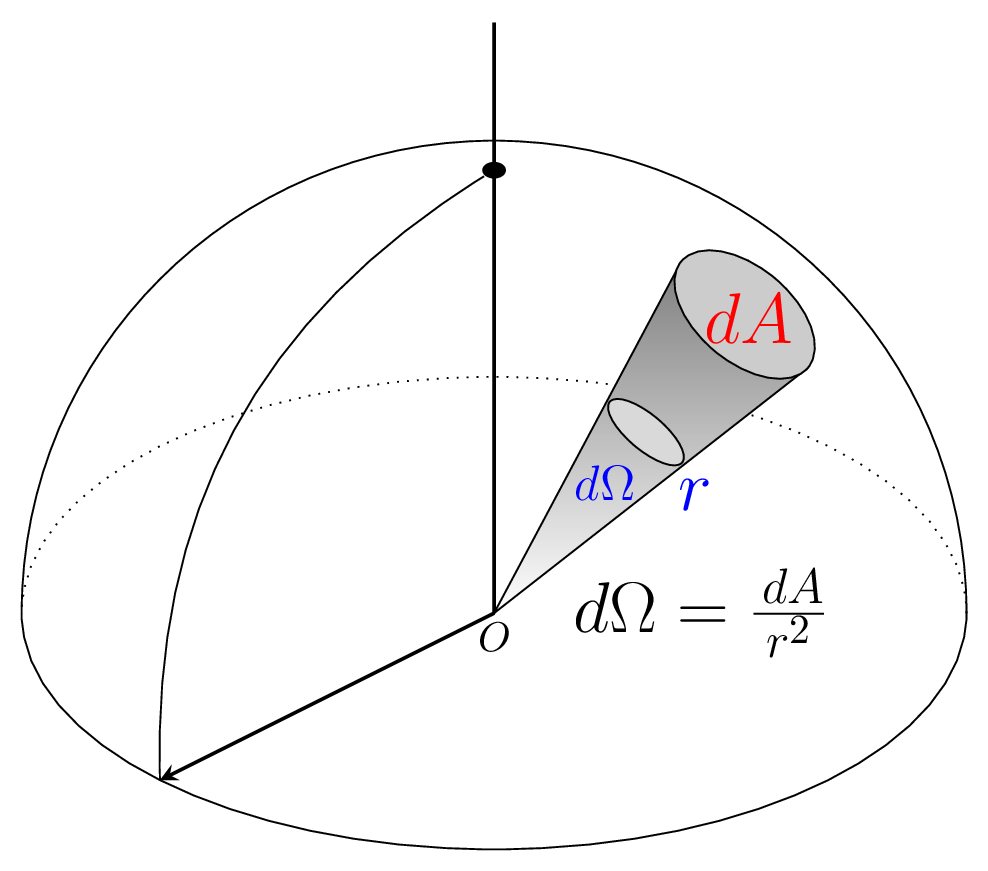
Definitions: A meter is the length of the path traveled by light in vacuum during a time interval of \(1/299,792,458\) second. Kilogram is the mass of a platinum-iridium alloy cylinder stored in the International Bureau of Weights and Measures at Saint-Cloud, France. A second is the time that elapses during \(9192631770\) cycles of a cesium-133 atomic clock. An ampere is the current which would produce a force \(2\times 10^{-7}\) Newton per meter if passes through two negligibly thin straight parallel conductors of infinite length when placed at 1 meter apart in vacuum. Kelvin is a temperature which defines the triple point of water as 273.16 K. A mole is the amount of substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in exactly 12 grams of carbon-12 isotope. One mole of anything is equal to Avogadro’s number. Candela is the intensity of a light source that emits monochromatic radiation of frequency \(540\times 10^{12}\) hertz and has a radiant intensity \(\frac{1}{683}\) watt per steradian in the same direction. Radian is the ratio of length of arc \(\,ds\) to the radius \(r\) of a circle [Figure 1.1.2.(a)]. Sterad is the ratio of the intercepted area \(\,dA\) of the spherical surface, described about the apex O as the center, to the square of its radius \(r\) [Figure 1.1.2.(b)].