Section 5.3 The Fourier Cosine and Sine Series
A function \(f(x)\) is said to be an even function if \(f(x)=f(-x).\) e.g., \(\cos x {,} \sec x {,} x^{2} {,} x \sin nx {,} \) etc. are even functions. The graph of such a function is symmetrical with respect to \(f(x)\) axis. The area under such a curve from \(-\pi\) to \(\pi\) is double the area from 0 to \(\pi\text{.}\)
\begin{equation*}
\therefore \int\limits_{-\pi}^{\pi}f(x)\,dx = 2\int\limits_{0}^{\pi}f(x)\,dx
\end{equation*}
here,
\begin{equation*}
a_{0}= \frac{1}{\pi}\int\limits_{-\pi}^{\pi}f(x)\,dx = 2\int\limits_{0}^{\pi}f(x)\,dx;
\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}
a_{n}= \frac{1}{\pi}\int\limits_{-\pi}^{\pi}f(x) \cos nx\,dx = \frac{2}{\pi}\int\limits_{0}^{\pi}f(x)\cos nx\,dx;
\end{equation*}
and
\begin{equation*}
b_{n}= \frac{1}{\pi}\int\limits_{-\pi}^{\pi}f(x) \sin nx\,dx = 0 \quad \text{[Half-Range Series]}
\end{equation*}
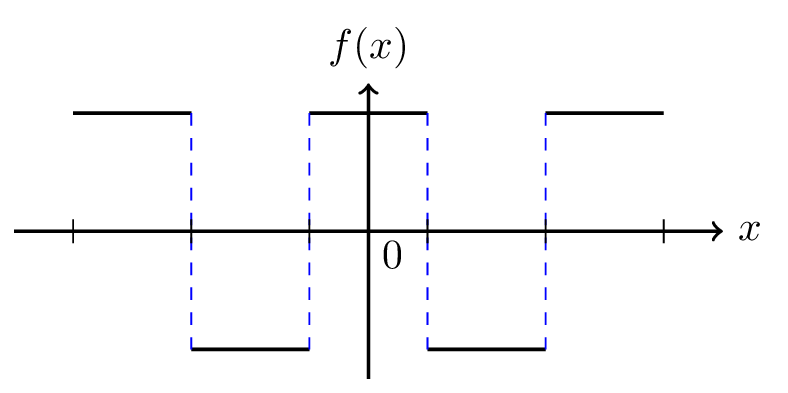
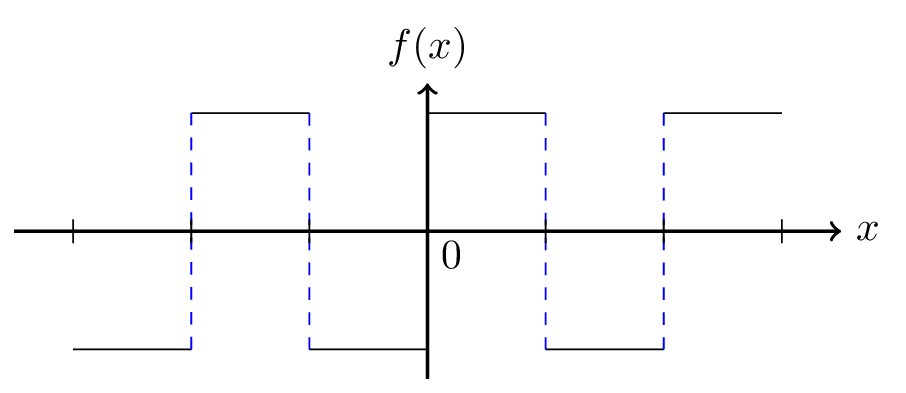
In this case, Fourier Series is represented by
\begin{equation*}
f(x) =\frac{a_{0}}{2}+\sum\limits_{n=1}^{\infty}a_{n} \cos nx
\end{equation*}
and is called Fourier cosine series as \(b_{n}=0\) for all the even function [figure Figure 5.3.1.(a)]. Again, a function \(f(x)\) is said to be an odd function if \(f(-x) = -f(x)\text{.}\) For example, \(x {,} \tan x {,}x^{3}{,} \sin x{,}\) etc. are odd functions. The graph of such a function is skew symmetrical with respect to \(f(x)\) axis. The area under such a curve from \(-\pi\) to \(\pi\) is zero. That is,
\begin{equation*}
\int\limits_{-\pi}^{\pi}f(x) \,dx =0;
\end{equation*}
here
\begin{equation*}
a_{0}= \frac{1}{\pi}\int\limits_{-\pi}^{\pi}f(x)\,dx = 0;
\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}
a_{n}= \frac{1}{\pi}\int\limits_{-\pi}^{\pi}f(x) \cos nx\,dx = 0;
\end{equation*}
and
\begin{equation*}
b_{n}= \frac{1}{\pi}\int\limits_{-\pi}^{\pi}f(x) \sin nx\,dx = \frac{2}{\pi}\int\limits_{0}^{\pi}f(x) \sin nx\,dx \quad \text{[Half-Range Series]}
\end{equation*}
In this case, Fourier series is represented by
\begin{equation*}
f(x) = \sum\limits_{n=1}^{\infty}b_{n} \sin nx
\end{equation*}
is called Fourier sine series as \(a_{0}\) and \(a_{n}\) are zero in all the odd function [figure Figure 5.3.1.(b)].
