Subsection 11.5.1 Human History
3
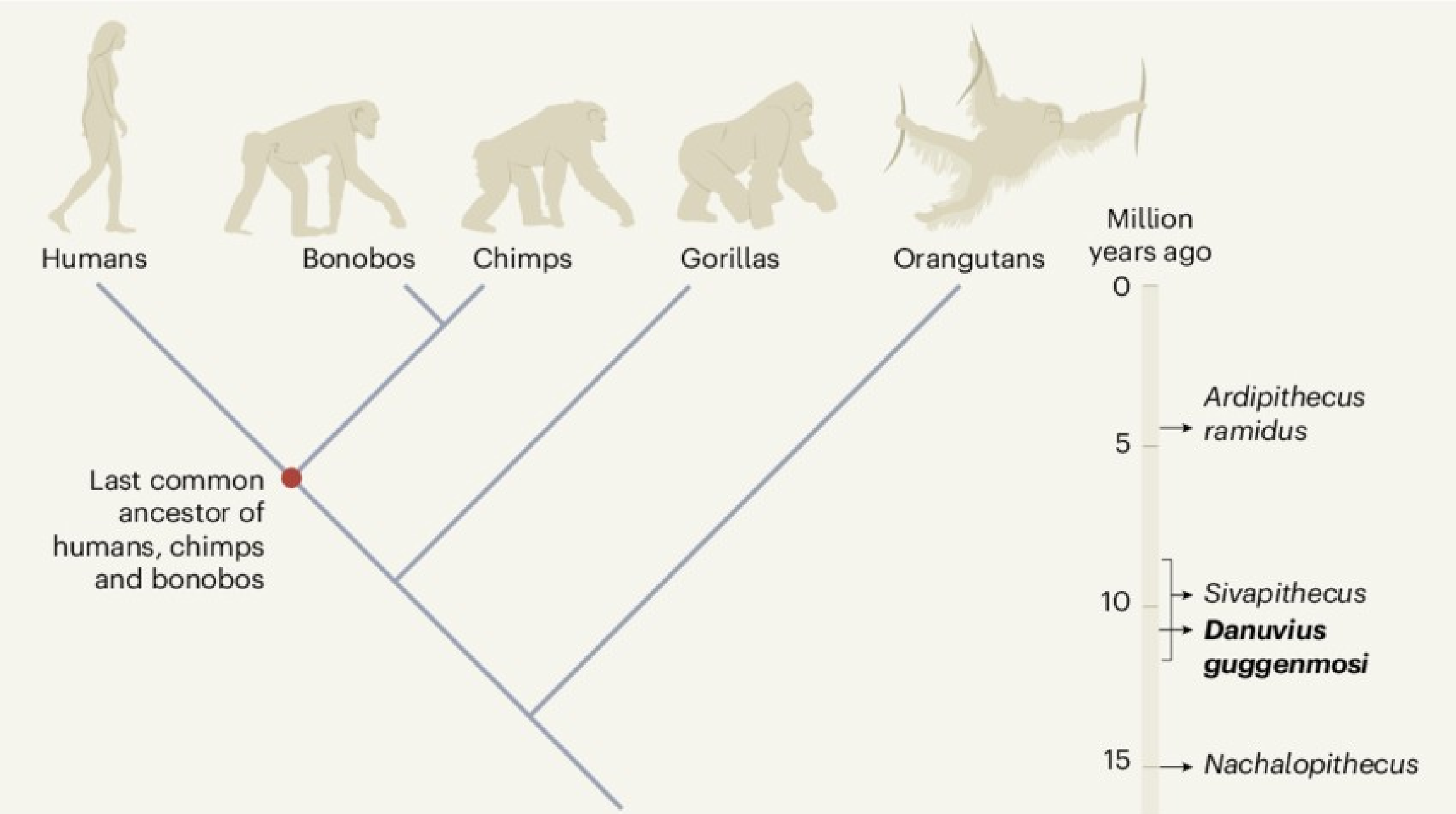
www.nature.com/articles/d41586-019-03347-0Human history is the study of the past experiences, actions, and achievements of human beings from ancient times to the present day. The Great Rift Valley has played a significant role in human history, as it is considered by many anthropologists and archaeologists to be the cradle of humanity. The region’s abundant resources and diverse landscapes have attracted human settlements for hundreds of thousands of years, and it has been the site of numerous important archaeological discoveries. The earliest evidence of human ancestors in the Great Rift Valley dates back to about 6 million years ago, with the discovery of Sahelanthropus tchadensis fossils in Chad. However, the most significant discoveries in the region are associated with the emergence of the Homo genus, which includes modern humans. Hominins are a group of primates that includes humans and our closest extinct relatives. The term "hominin" is used to describe all species that belong to the human lineage since it split from the lineage that led to himpanzees and bonobos, our closest living relatives.
