Subsection 11.3.1 Types of Deformation
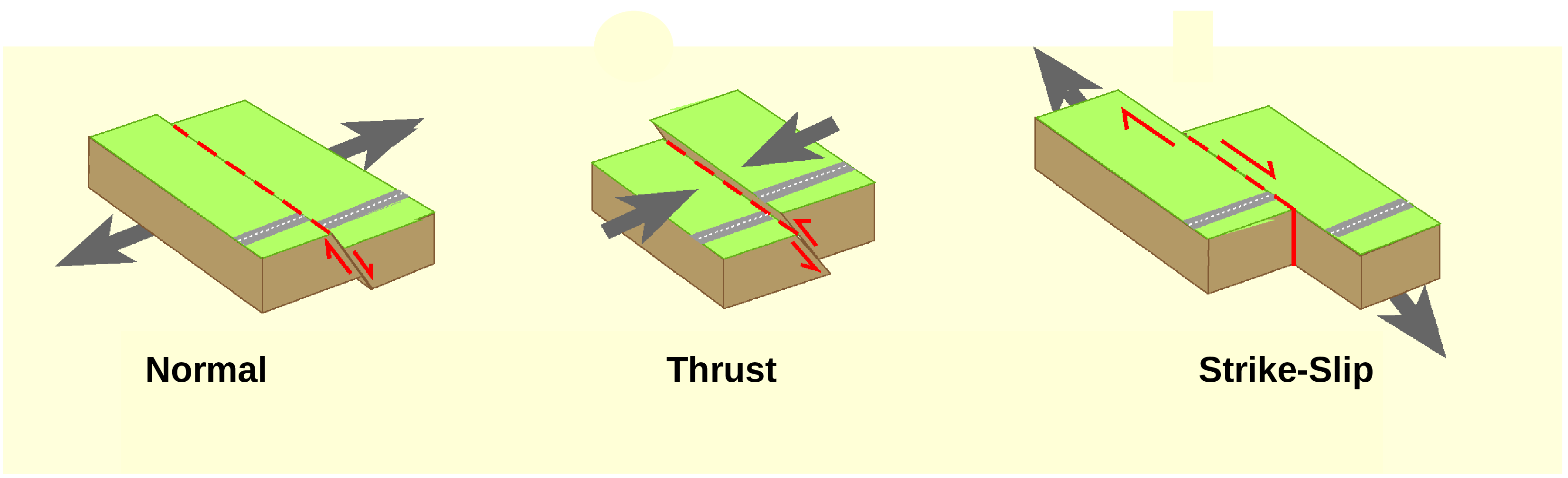
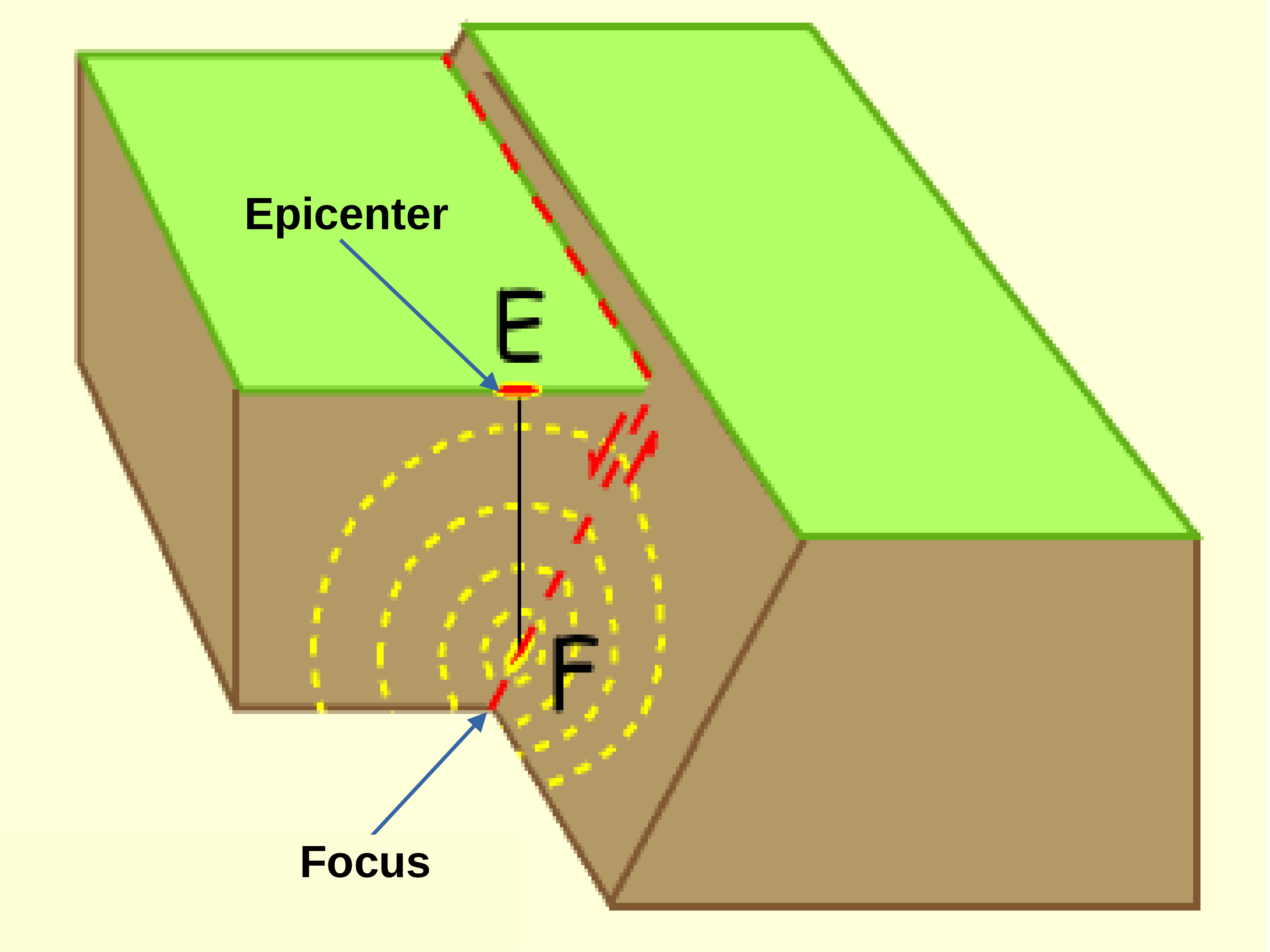
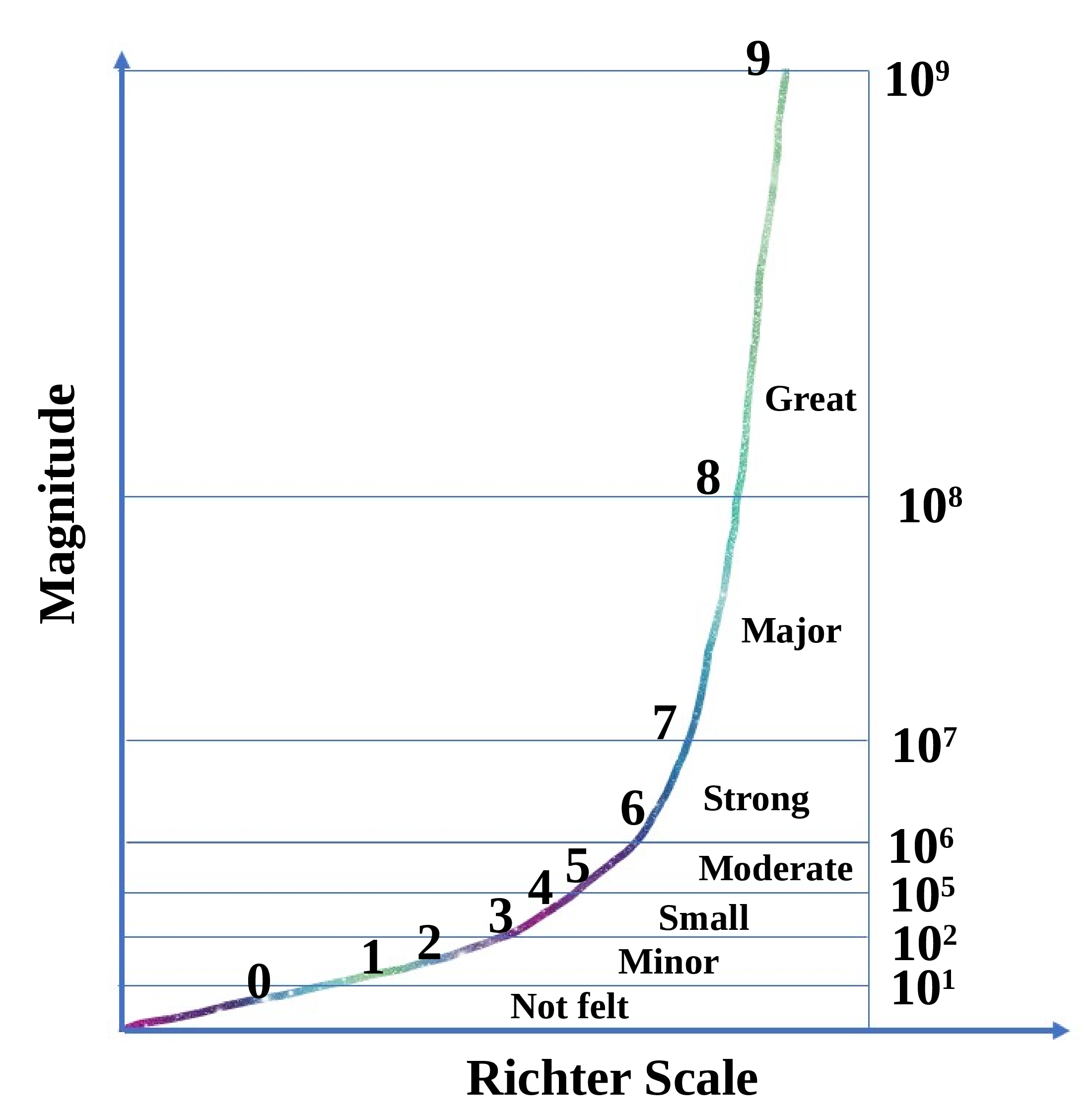
There are many types of structural deformation happens on the earth surface. They are faults, folds, warps, tilts, rises, and falls. A Fault is a fracture, crack, or break in the Earth’s crust along which earth’s plates move relative to each other. Faults can be classified as either dip-slip faults, where the movement is vertical, or strike-slip faults, where the movement is horizontal. Here are some of the most common types of faults: Normal fault: occurs when two blocks of rock are pulled apart, causing one block to drop down relative to the other. Normal faults are common in areas where the Earth’s crust is being stretched, such as at divergent plate boundaries. Reverse (or, thrust) fault: occurs when two blocks of rock are pushed together, causing one block to be pushed up relative to the other. Reverse faults are common in areas where the Earth’s crust is being compressed, such as at convergent plate boundaries. Strike-slip fault: occurs when two blocks of rock slide past each other horizontally. Strike-slip faults are common in areas where the Earth’s crust is being sheared, such as at transform plate boundaries. Thrust fault: is a type of reverse fault in which the angle of the fault plane is shallow. Thrust faults are common in areas where the Earth’s crust is being compressed, such as in mountain ranges. Faults are seen in Figure 11.3.4.(a). Folds: A fold is a bend or curve in the Earth’s crust that results from compressional forces. Folds can be classified as either anticlines, where the rock layers arch upwards, or synclines, where the rock layers fold downwards. Tilts: A tilt is a change in the angle of the Earth’s crust relative to the horizontal. Tilts can be caused by various forces, including tectonic movements and the deposition of sedimentary layers. Warps: A warp is a broad upward or downward deformation of the Earth’s crust. Warps can be caused by tectonic forces or the weight of overlying sedimentary layers. The rise and fall of the Earth’s surface can occur due to tectonic activity, volcanic activity, erosion, and sedimentation. In tectonic activity, When plates collide or move apart, they can cause the Earth’s surface to rise or fall. For example, the collision of the Indian and Eurasian plates caused the Himalayan Mountains to rise.
