Section 9.2 Solution
A solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of two or more substances. The substance that dissolves is called the solute, and the substance that does the dissolving is called the solvent. When the solute dissolves in the solvent, the resulting solution is a uniform mixture, called solution.
\begin{equation*}
Solute + Solvent = Solution
\end{equation*}
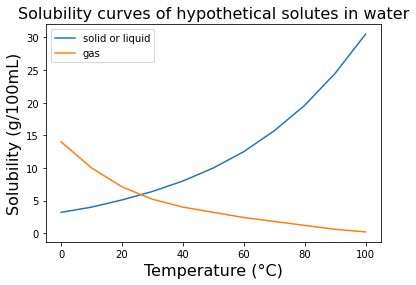
Solubility is the ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent to form a solution. The solubility of a substance depends on various factors such as temperature, pressure, and the nature of the solute and solvent. In general, "like dissolves like," meaning that substances with similar chemical properties tend to dissolve in each other. The amount of solute that can dissolve in a given amount of solvent is limited by the solubility of the solute in the solvent. When a solution contains the maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in the solvent at a given temperature and pressure, is said to be a saturated solution. If more solute is added to a saturated solution, it will not dissolve and will form a separate phase, such as a solid precipitate or gas bubbles.
Concentration: The concentration of a solution is the amount of solute dissolved in a specific amount of solvent or solution. The term "saturated" and "unsaturated" are used to describe the concentration of solute in a solution. A saturated solution contains maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in a given solvent at a particular temperature and pressure. No more solute can be dissolved in the solvent of the saturated solution without increasing the temperature or pressure. Any additional solute added to the solution will not dissolve and will remain as a solid. On the other hand, an unsaturated solution contains less than the maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in a given solvent at a particular temperature and pressure. In an unsaturated solution, more solute can be added and dissolved in the solvent. It’s important to note that a solution can also be supersaturated , which means it contains more solute than what can theoretically be dissolved at a given temperature and pressure. Supersaturated solutions are not stable and can spontaneously crystallize, forming a precipitate, or solid, out of excess solute.