Section 7.2 Nuclear Structure
The nucleus contains protons and neutrons. The protons are positively charged particles and the neutrons have no charge. Nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons collectively known as known as nucleons. The nucleons are held together by the strong nuclear force. Strong nuclear force is a very short-range attractive force that acts between nucleons and helps keep the nucleus from flying apart due to the repulsive force of the positively charged protons. The different number of neutrons in a nucleus of the same element forms the isotopes isotopes of the atom. Isotopes are atomic species of an element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons in the nucleus. That is the isotopes of an element have the same atomic number but a different atomic mass, hence isotopes can have different physical and chemical properties. Some isotopes are stable and do not undergo radioactive decay, while others are radioactive and decay over time. Age of rocks, fossils, and evolution of the universe can be determined by using isotopes. Here is the isotopic natation of the nucleus.
\begin{equation}
{}_Z^AX\tag{7.2.1}
\end{equation}
where \(X\) = chemical symbol of element, \(Z\) = atomic number of element, and \(A\) = mass number of nucleus = number of protons and neutrons in nucleus. Therefore the number of neutron, \(N=A-Z\text{.}\)
There are over 3,000 known isotopes in the periodic table, but not all of them are naturally occurring. Some isotopes are stable and do not undergo radioactive decay, while others are radioactive and decay over time. The number of isotopes of an element can vary greatly, with some elements having only one or two isotopes, while others have many. The lightest element hydrogen has three isotopes Figure 7.2.1. They are Hydrogen: \({}_1^1H\text{,}\) Deuterium: \({}_1^2H\text{,}\) and Tritium: \({}_1^3H\text{.}\) Heavy water is a type of water molecule that contains a heavier isotope of hydrogen, deuterium (H-2) instead of the common hydrogen isotope (H-1). Heavy water has the same chemical properties as regular water \((H_2O)\text{,}\) but its physical properties, such as boiling and melting points, are slightly different. Heavy water is used in various industrial and scientific applications, including nuclear reactors, where it serves as a moderator to slow down the speed of neutrons in the reactor core.
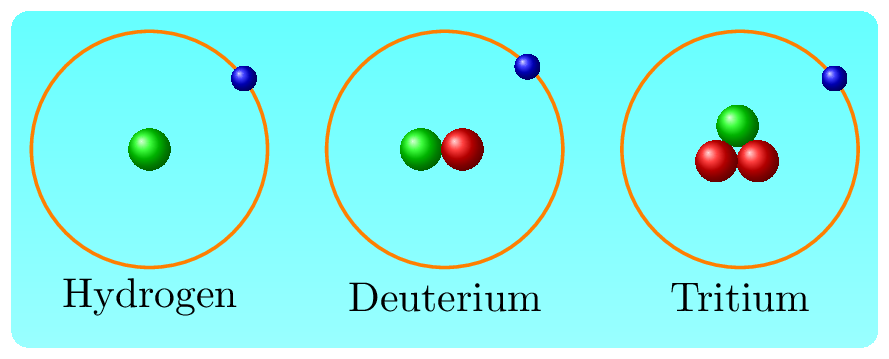
The isotopes of hydrogenCarbon is an element that has several isotopes. Some of them are carbon-12 (or, \({}_6^{12}C\)) and carbon-13 (or, \({}_6^{13}C\)), and carbon-14 (or, \({}_6^{14}C\)). Carbon-12 and carbon-13, are naturally occurring isotopes and make up the majority of carbon on Earth. Carbon-12, has 6 protons and 6 neutrons and is the most abundant in nature. Carbon-12 is considered the standard for atomic mass. Carbon-13, has 6 protons and 7 neutrons and is a stable isotope. Carbon-13 makes up about 1% of the total carbon on Earth. Carbon-14 is a naturally occurring isotope that is produced in the Earth’s atmosphere through cosmic radiation and is taken up by living organisms. It is used in the radiocarbon dating method to determine the age of organic materials and is an important tool in archaeology and other fields.
