Section 9.1 Crystalline Solids


On the basis of chemical bonding there are four main types of crystalline solids:
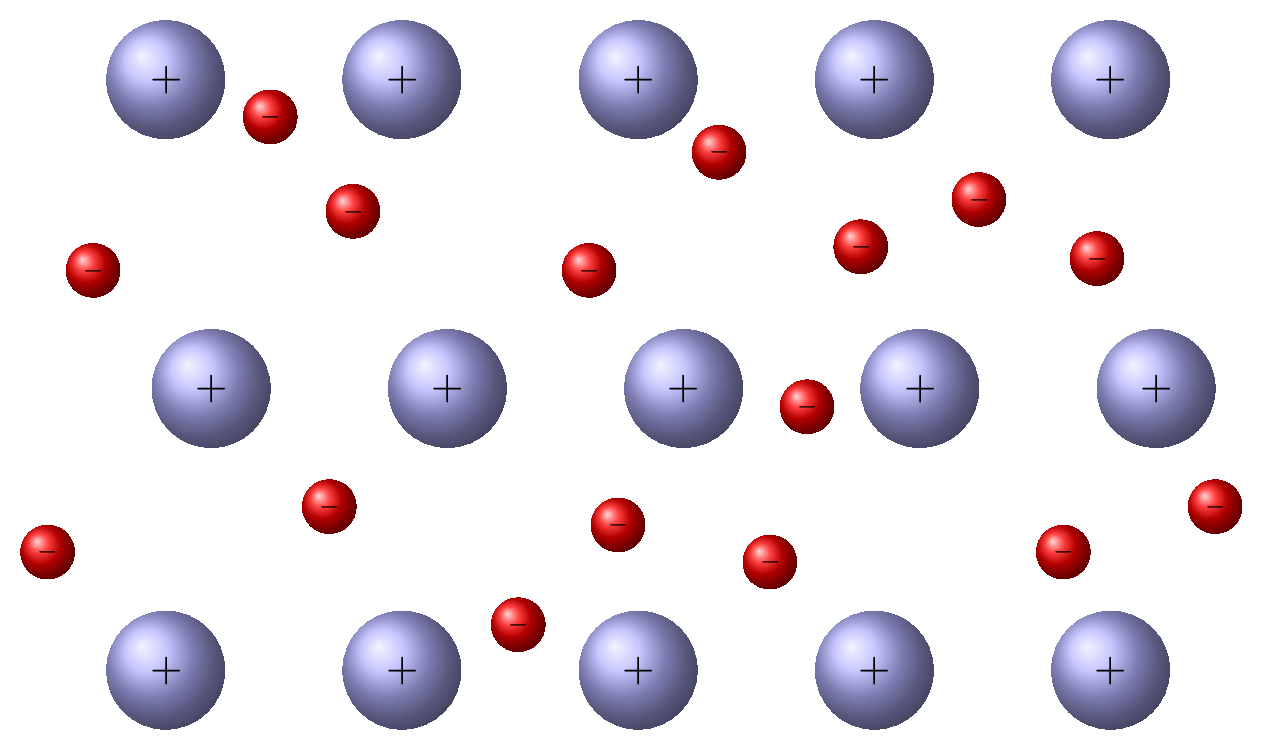
- Ionic solids: These solids are made up of positively charged ions and negatively charged ions held together by electrostatic forces. These molecules are hard and posses high melting point. Examples include sodium chloride (NaCl) and calcium fluoride \((CaF_2)\) [Figure 9.0.1.(a)].
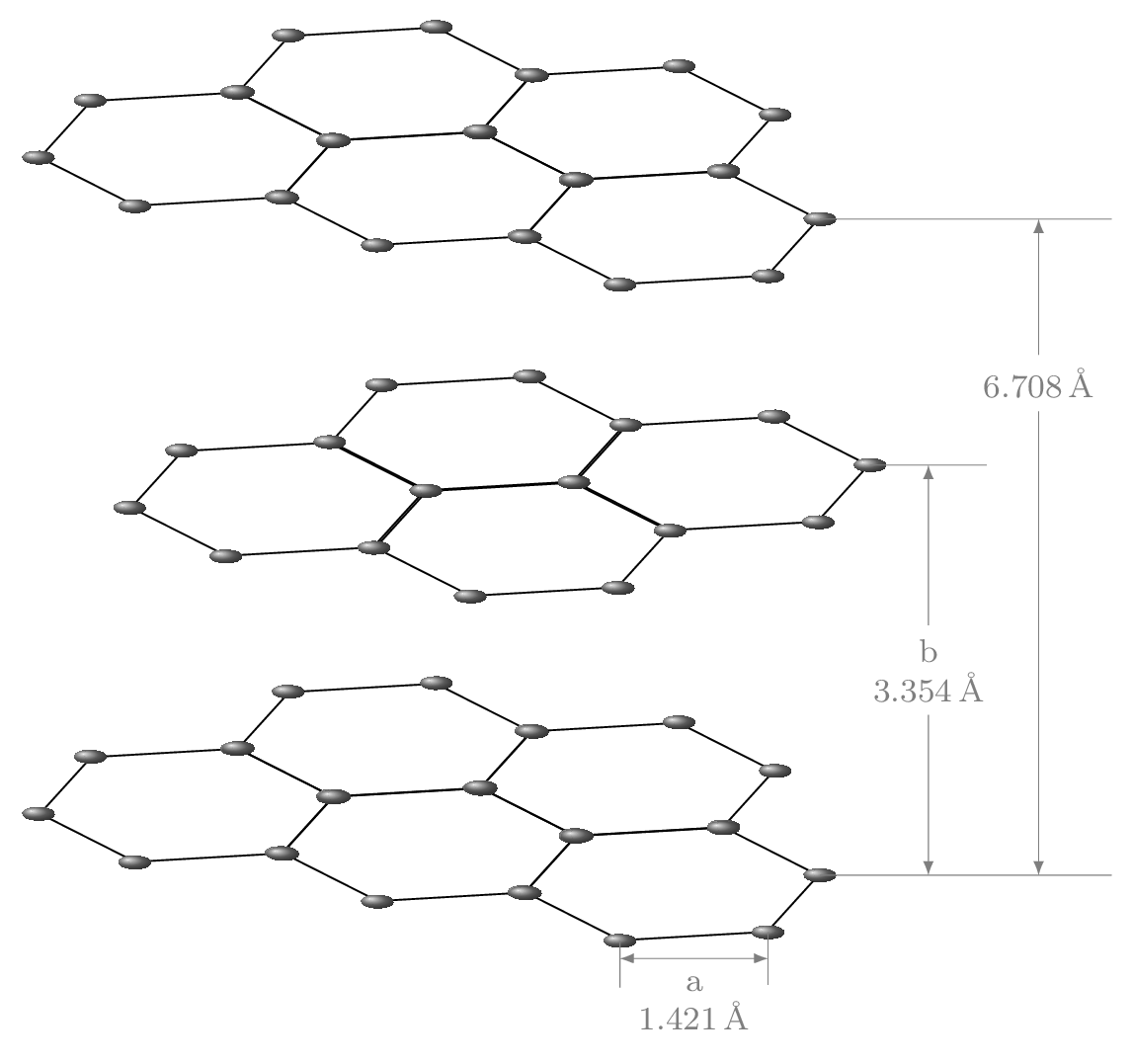
- Covalent solids: These solids are made up of atoms held together by covalent bonds. These molecules are very hard and posses very high melting point. Examples include diamond [Figure 9.1.1.(a)] and graphite [Figure 9.1.1.(b)].
- Metallic solids: These solids are made up of metal atoms held together by metallic bonds. These molecules can be deformed, have metallic luster, high electrical and thermal conductivity. Examples include copper, iron, and gold. [Figure 9.1.1.(c)]
- Molecular solids: These solids are made up of molecules held together by intermolecular forces such as hydrogen bonds, van der Waals forces, and dipole-dipole interactions. These molecules are soft and posses low melting point. Examples include ice \((H_2O) \) and solid carbon dioxide \((CO_2)\) [Figure 9.1.1.(d)].
