Skip to main content\(\newcommand{\N}{\mathbb N}
\newcommand{\Z}{\mathbb Z}
\newcommand{\Q}{\mathbb Q}
\newcommand{\R}{\mathbb R}
\newcommand{\T}{\mathcal T}
\newcommand{\lt}{<}
\newcommand{\gt}{>}
\newcommand{\amp}{&}
\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}
\newcommand{\fillinmath}[1]{\mathchoice{\colorbox{fillinmathshade}{$\displaystyle \phantom{\,#1\,}$}}{\colorbox{fillinmathshade}{$\textstyle \phantom{\,#1\,}$}}{\colorbox{fillinmathshade}{$\scriptstyle \phantom{\,#1\,}$}}{\colorbox{fillinmathshade}{$\scriptscriptstyle\phantom{\,#1\,}$}}}
\)
Section 6.3 Examples
Example 6.3.1.
The speed of sound is fastest in
liquids.
solids.
gases.
vacuum.
Example 6.3.2.
The frequency of a sound determines its quality and the amplitude of the sound determines its .
timber.
frequency.
loudness.
pitch.
Example 6.3.3.
which wave given below is partly longitudinal and partly transverse?
light wave.
sound wave.
water wave.
string wave.
Example 6.3.4.
When a wave goes from one medium to another medium, which quantity of wave does not change?
frequency.
speed.
amplitude.
wavelength.
Example 6.3.5.
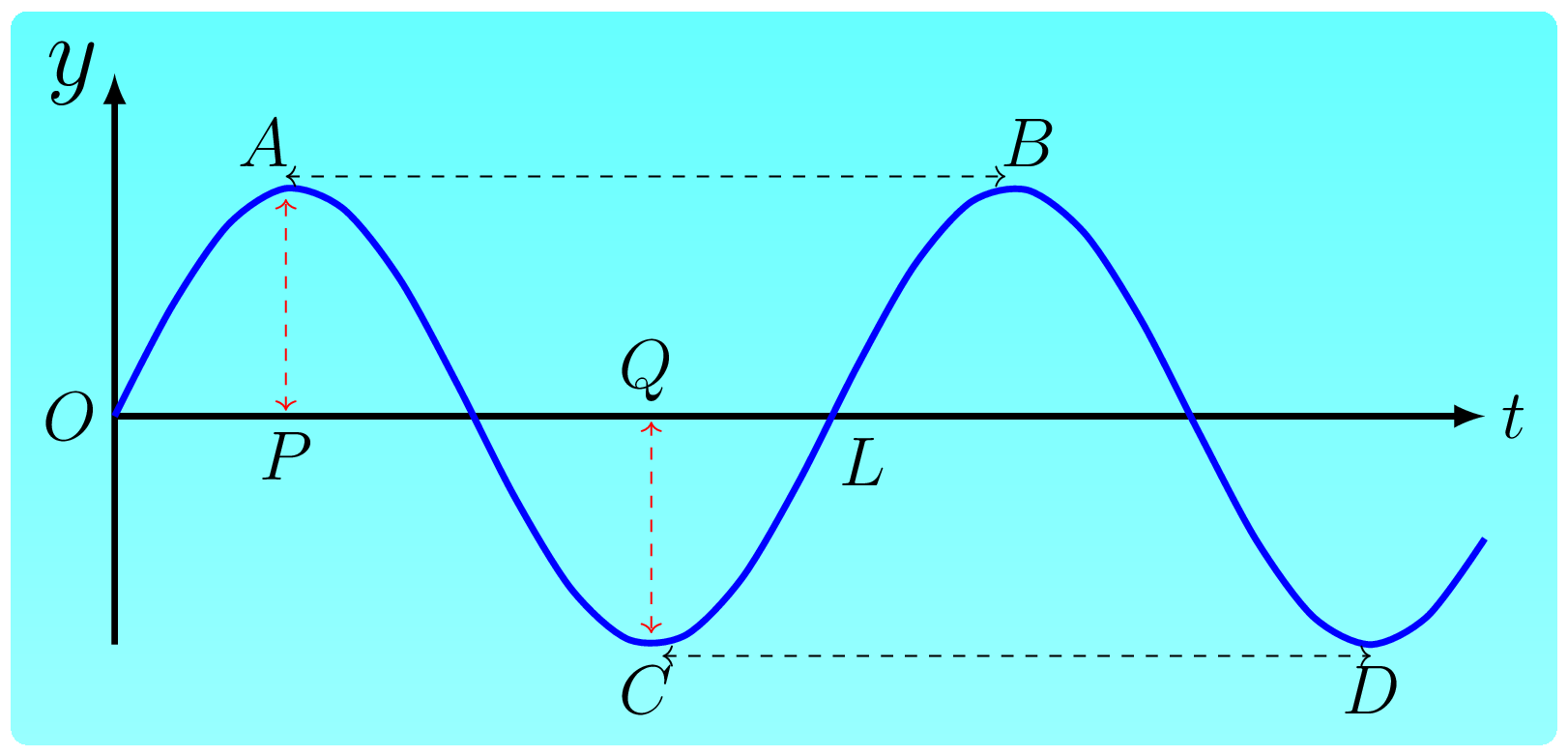
Indicate the amplitude of a wave in the figure below.
Figure 6.3.6.
PA.
QC.
AB.
CD.
Select one of the following.
Both I and II
Both III and IV.
I only.
III only.
Example 6.3.7.
Indicate the wavelength of a wave in the figure below.
Figure 6.3.8.
PA.
QC.
AB.
CD.
Select one of the following.
Both I and II
Both III and IV.
I only.
III only.
Example 6.3.9.
How far inside the plane mirror your image appears?
As far as I am standing infront of the mirror.
Just double the distance I am standing infront of the mirror.
Cannot be determined.
depends upon my size.
Example 6.3.10.
What causes the pool of water appears to be less deep than it actually is
Reflection.
Refraction.
Dispersion.
Scattering.
Example 6.3.11.
What causes light to refract to form rainbow in the sky?
glass prisms.
sunlight rays
small raindrops
air molecules.
Example 6.3.12.
why does the fork look larger under water?
light is refracted at an angle.
light cannot pass through the glass.
the amount of light increases when going through water.
the wavelength of light increases in the process.
Example 6.3.13.
When light passes through a prism the light splits into the visible spectrum. What color bends the most and has the shortest wavelength?
red.
violet.
yellow.
blue.
Example 6.3.14.
The color of object you see is the color that is
absorbed by the object.
reflected by the object.
Example 6.3.15.
What is the speed of wave which completes one full cycle in \(10 \,s\) and has a wavelength of \(120\, m\text{?}\)
Answer.
Solution.
Given: \(T=10 s\text{,}\) \(\lambda = 120 \,m\text{,}\) \(v=?\)
\begin{align*}
v \amp =f\lambda
\end{align*}
\begin{align*}
f \amp =\frac{1}{T} \\
\therefore v \amp =\frac{\lambda}{T} = \frac{120 m}{10 \,s}
\end{align*}